Project Smart4Module
Excerpt
Smart reductions in the environmental impact of photovoltaic modules: interconnection, encapsulation and integration.
Romain Feilleux-Anginieur, Laboratory Manager, CEA
ANR reference : 22-PETA-0006
The Smart4Module project explores several avenues for reducing the environmental impact of the photovoltaic industry. Specifically, the focus is on developing materials and processes that can reduce the use of critical materials and/or facilitate their recycling. By extension, the issue of land use is also being addressed through integration into already artificial surfaces. The project’s contributions will focus on the modulization of various cell technologies. As such, particular attention will be paid to the reliability and durability of the proposed solutions, where possible. The topics covered are divided along the three axes of module manufacture: interconnection, encapsulation and integration.
Key words: Photovoltaic modules, encapsulation, interconnection, integration, reduction of critical materials, recycling, acceptability, durability, reliability.
Tasks
Our researches
Interconnection
Inside a module, the cells are electrically connected to each other. This connection generally uses diodes and interconnections, which currently rely on the use of critical materials. What’s more, the processes used are not systematically compatible with new cell technologies. The Smart4Module project will contribute to the development of diode manufacturing processes compatible with module printing. Next, efforts will be made to develop two interconnection technologies without critical materials, using organic solutions.
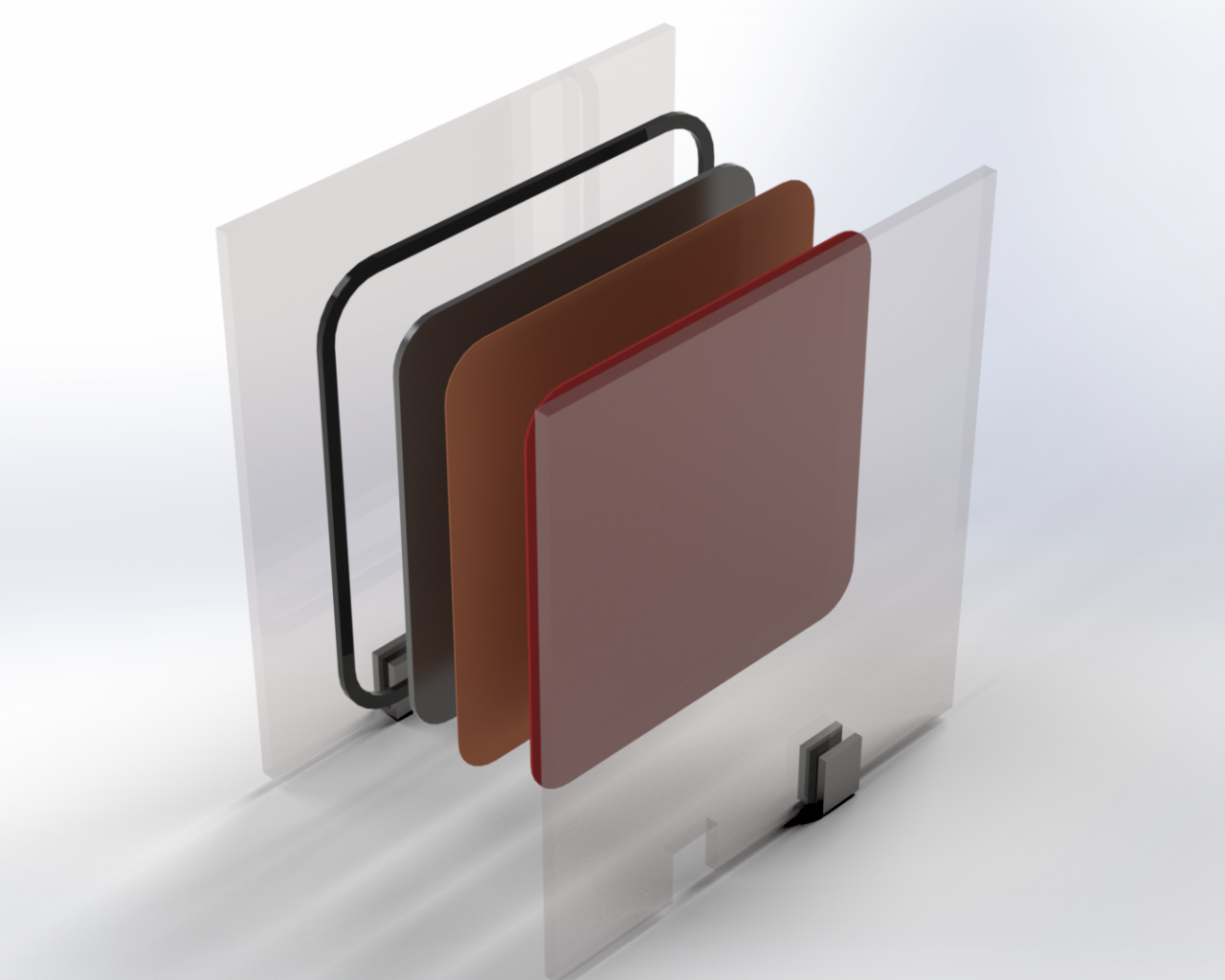
Encapsulating
Encapsulating photovoltaic cells protects them from the external environment (humidity, oxygen, mechanical stress, etc.). At present, the processes and materials used give rise to a number of problems. In particular, encapsulation makes it particularly difficult to recycle panels at the end of their life, and the level of protection against moisture penetration is insufficient for future cell technologies. The Smart4Module project aims to develop new encapsulation materials that reconcile reliability and recyclability. At the same time, efforts will be made to develop new encapsulation processes compatible with new cell technologies and offering enhanced protection against moisture penetration.
Integration
The deployment of photovoltaics poses the problem of competing land uses. At present, this problem is addressed in a number of ways, including integration with agricultural land (agrivoltaics) and integration with buildings (BIPV). The Smart4Module project will contribute to the development of new transparent or semi-transparent solutions adapted to these modes of integration. These solutions will respectively aim to selectively use the solar spectrum for agrivoltaic applications, and to facilitate social acceptance for BIPV.
Consortium
The consortium includes 14 CNRS mixed units, 2 CEA laboratories and 2 engineering schools.
The Smart4Module project deals with a number of technological issues relating to the materials and processes used to package modules. Behind this set of technical issues lies a collection of open scientific questions.
For example, when it comes to encapsulation, reliability and ease of recycling are, a priori, incompatible. By using new types of materials, processes or other means that reconcile the two, and which have hitherto been little or not used in photovoltaics, new technical questions will arise. Dealing with them using the scientific method should lead to scientific contributions in materials science, chemistry, mechanics and so on.
The aim of the Smart4Module project is to identify these issues and provide answers to the feasibility and viability of the proposed solutions, while contributing to the scientific corpus of the fields involved.


No news
More projects


